
Batteries of the future: with scientific advancements accelerating at an unprecedented pace, it’s nearly impossible to know exactly what the technology of the future will look like. Daniel Cardona
By Mariana Meneses
As the world becomes more environmentally conscious, the growing demand for cleaner technological tools such as electric vehicles is driving the need for more high-value metals like cobalt, nickel, and lithium for batteries to power them.
However, this surge in demand also raises significant concerns about depletion of scarce resources, environmental damage, and waste from non-recyclable components. As a result, scientists are exploring sustainable solutions, by recycling and developing new, greener technologies that rely on more readily available materials.
For instance, as noted by Casey Crownhart, for the MIT Technology Review, recycling lithium-ion batteries offers a sustainable solution to meet the rising demand for their metals while reducing the need for new mining operations.
Lithium-ion batteries are widely used in many devices, including smartphones, laptops, and electric cars, due to their high energy density and relatively low weight.
However, these batteries have several issues that need to be addressed. One of the main problems is the risk of uncontrolled heat buildup in the battery chemicals that results in thermal runaway, which can cause fires and explosions due to overcharging, overheating, or physical damage to the battery. Additionally, there are concerns about supply chain sustainability of the materials used in these batteries, such as cobalt and nickel. Lithium-ion batteries also have limited lifetimes, with performance degradation occurring after a certain number of charge cycles, and they can take a long time to recharge.
Finally, the disposal of these batteries can lead to environmental problems, as they contain toxic chemicals that can leach into soil and water if not properly disposed.
We highlight four research projects related to sustainable and environmentally friendly battery technologies that could potentially replace traditional lithium-ion batteries.
Each project focuses on a different aspect – including the development of organic electrode materials, the improvement of seawater batteries, the exploration of fiber-shaped cathodes for zinc-ion batteries, and the enhancement of the power, safety, and eco-friendliness of zinc batteries – all with the aim of creating a more sustainable and cost-effective energy storage solution.
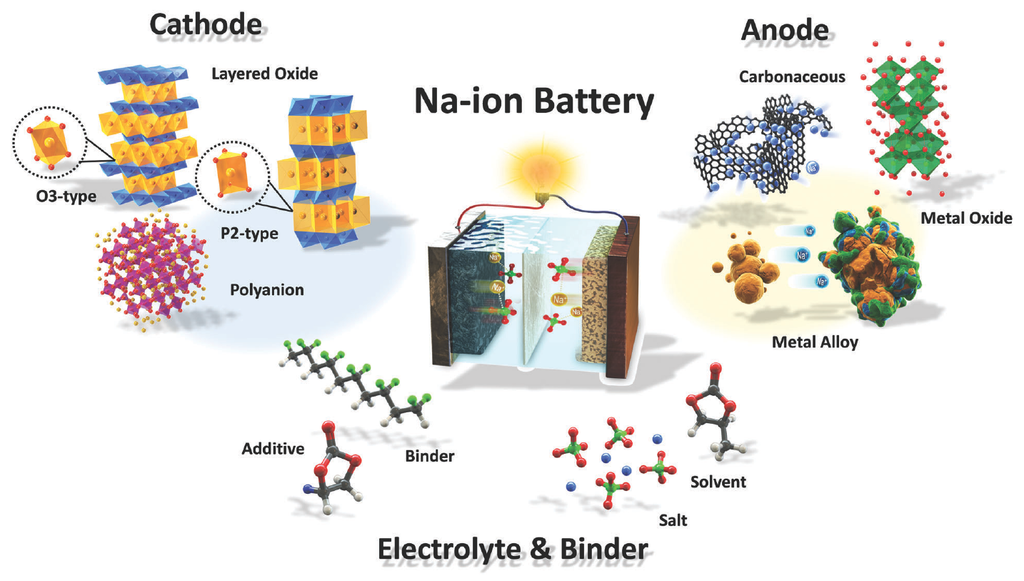
Researchers led by Dr. Yuan Chen, from the University of Sidney, are exploring sustainable and cost-effective organic batteries with redox-organic electrode materials made from natural sources which have high capacity and can be easily recycled.
Redox, short for reduction-oxidation, is a chemical reaction where atoms change their oxidation states by one substance losing electrons (oxidation) and another gaining electrons (reduction). In organic chemistry, redox-organic reactions involve changes in the gain of oxygen and/or loss of hydrogen in organic compounds, even if direct electron transfer is not always involved.
Inorganic batteries face issues of limited resources, toxicity, environmental problems, and high costs. Organic batteries with redox-organic electrode materials can store and release energy through redox reactions, similar to the way inorganic materials like lithium-ion do. However, they are made from natural resources, which makes them a promising renewable energy solution.
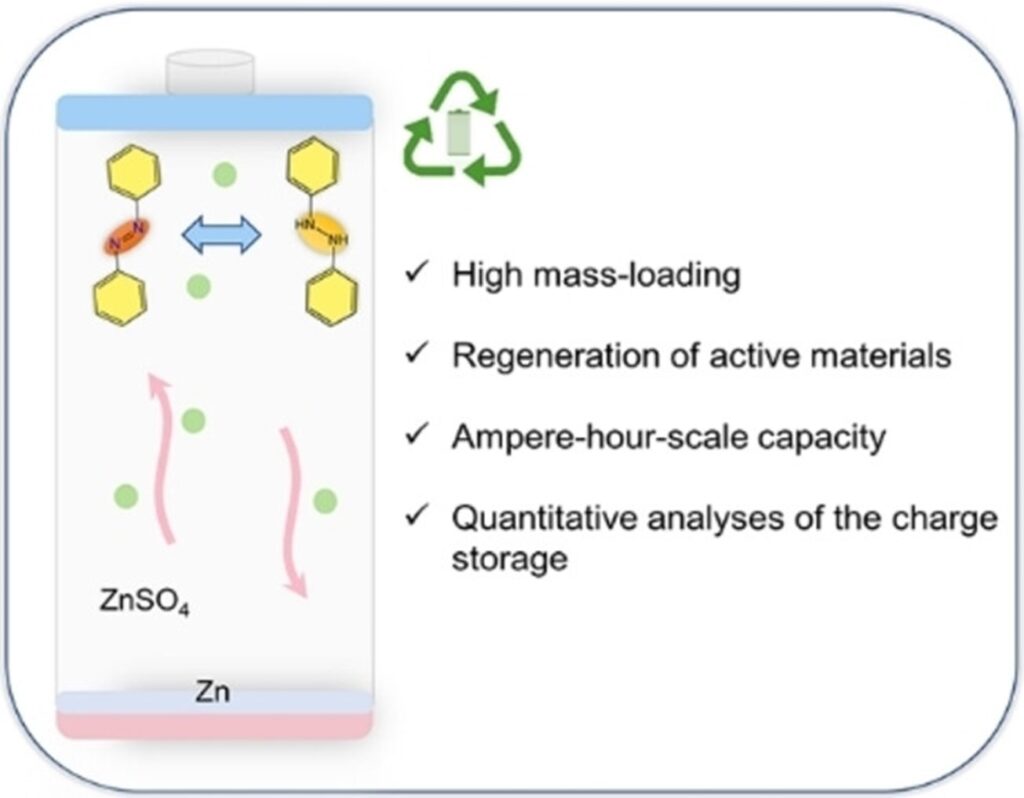
A new organic material has been suggested for large aqueous batteries that can provide a high capacity of electric charge. Credit: Chen, Yuan, et al. (2023).
The new organic electrode material uses azobenzene for aqueous organic high-capacity batteries, which means that water is used as the solvent in the electrolyte, the medium that enables the flow of electric charge between the cathode and anode.

Another recent development in battery research involves seawater. Photo: Pixabay .
Azobenzene is relatively inexpensive and can dissolve in certain liquids but not water. The electrode material can store a significant amount of energy because of how the azobenzene moves electrons. It’s also easy to recycle the battery by removing the azobenzene with commercial organic solvents. The battery is better for the environment and can be reused almost completely, making it a promising alternative to traditional rechargeable batteries.
The ocean presents a vast potential for generating environmentally friendly energy. Seawater batteries (SWB) are an emerging technology that can harness the ocean’s energy to produce electricity without harmful emissions.
In a 2023 study, researchers led by Hyebin Jeong, from Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), have improved seawater battery performance by incorporating chelating agents. Chelating agents are chemicals that can create stable, water-soluble compounds with metal ions.
These agents reduce defect generation rates, increasin energy efficiency, and capacity. Through their research, the team found that SWBs using chelating agents exhibited remarkable capacity retention rates of approximately 92.8%, and the potential for a sustainable and cost-effective energy storage solution.
The emergence of rechargeable seawater batteries was discussed in a 2019 paper by S. T. Senthilkumar and co-authors. These batteries are a new electrochemical system for storing electrical energy which uses seawater as a source of sodium ions for their cathode, which is the electrode from which the current leaves the polarized electrical device.
In the charging phase, sodium ions shift from the cathode to the anode as electrons flow through the external circuit, with the reverse happening during discharge. Image: Hwang et al.
While these technologies are still in the early stages of development and face technical and economic challenges, they have the potential to play a significant role in the transition to a cleaner energy future.
However, it is important to ensure that any ocean-based energy solutions are developed in a sustainable manner that does not harm marine ecosystems or disrupt local communities.
The researchers at POSTECH have made significant strides in improving SWB performance by incorporating chelating agents. This breakthrough in SWB performance could pave the way for the development of next-generation energy storage systems. The utilization of seawater batteries in energy storage could offer a sustainable and cost-effective alternative to current energy storage solutions. Moreover, their easy resource accessibility and environmentally friendly nature make SWBs an attractive option for the future of energy storage.
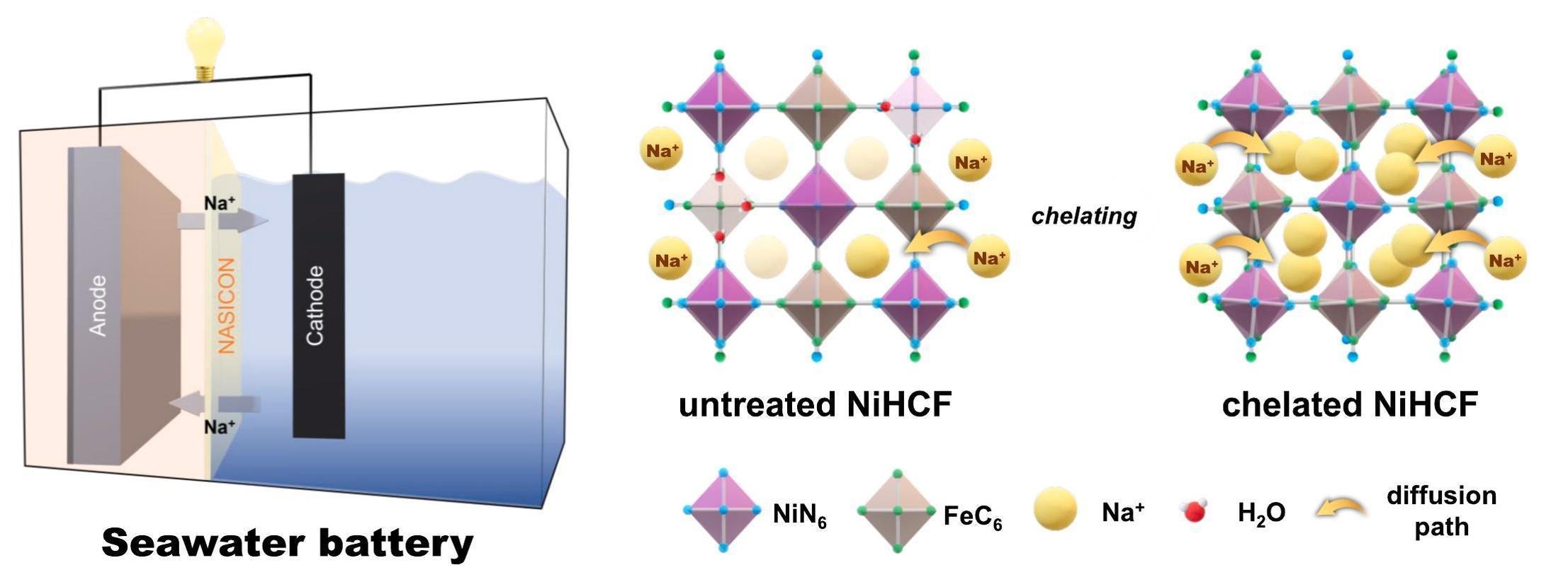
The study discovered that adding a special chemical to the cathode material in seawater batteries makes them work better and last longer, up to 2000 times, with almost all of their capacity remaining. Credit: eong, H. et al. (2023).
And there is more.
In another 2023 paper, researchers at North Carolina State University led by Nakarin Subjalearndee, from the National Nanotechnology Center, Thailand, reported the development of a proof-of-concept study of a fiber-shaped cathode for a zinc-ion battery prototype that can power a wristwatch, with hopes of integrating batteries into garments for wearable technology.
The study used graphene oxide with manganese dioxide particles to create a yarn-shaped zinc-ion battery. They made fibers with different sizes and shapes of manganese dioxide particles using a solution-spinning process. The scientists found that the shape of the materials affected the battery’s function, and they created a functional prototype. They then studied the electrochemical and other properties of the fibers.
Creating a yarn-shaped battery that can be integrated into garments and hidden from view would represent a significant step forward in the development of wearable technology, as current batteries are bulky and not conducive to integration with clothing.

Wearable technology tends to become more popular due to its convenience and ability to track and monitor various aspects of daily life. Photo: Create Health.
Finally, there have also been recent developments in zinc batteries.
Zinc batteries have emerged as a promising alternative to expensive and flammable lithium-ion batteries that are commonly used in mobile phones and electric vehicles.
However, these batteries face durability challenges due to issues such as hydrogen gas formation (i.e. when water in the battery’s electrolyte decomposes) and dendrite formation during charging. Dendrites are small, tree-like metal growths that can lead to battery failure over time. These challenges can lead to short battery life, safety concerns, and reduced performance.
To address these challenges, researchers led by Dario Gomez Vazquez, of the Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering at ETH Zürich, have developed a strategy to make zinc batteries more powerful, safer, and environmentally friendly, which could make them a better alternative to lithium-ion batteries. The findings were published in a 2023 paper.
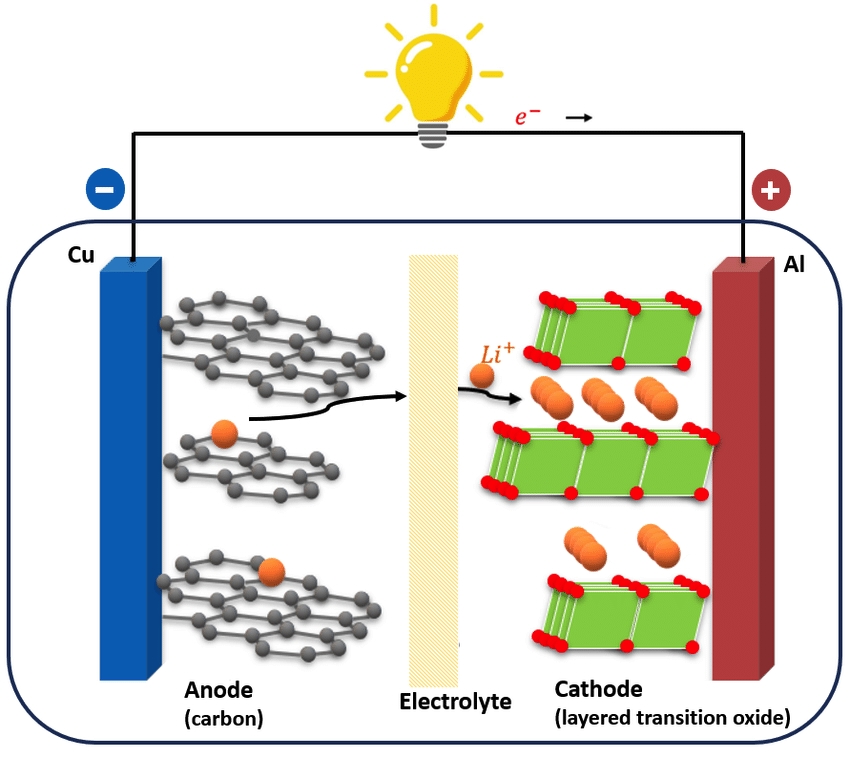
“A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery which uses the reversible reduction of lithium ions to store energy.” Source: Spitthoff et al.
The researchers found that a low concentration of acetates, rather than toxic salts, was ideal for the electrolyte fluid.
The electrolyte fluid is the medium that contains ions and transmits electricity through their movement, allowing for faster charging and discharging of the batteries.
The researchers successfully tested their strategy on a laboratory scale and plan to scale it up to determine if it can be applied to large batteries, potentially for use as storage units in the power grid or in homes for solar power storage. However, the team notes that optimizing cathode materials is still necessary for long-lasting and efficient zinc batteries.
Despite this challenge, the team’s work represents a significant step towards the development of safer, more powerful, and more environmentally friendly zinc batteries, which could have far-reaching implications for the energy storage industry and make zinc batteries a more viable alternative to lithium-ion batteries that currently dominate the market.

Fostering a sustainable way of living is crucial for the survival of our species in the long term. Tom Clohosy Cole
These four examples are strong evidence of an exciting and promising future for battery technology, as researchers continue to explore sustainable and cost-effective energy storage solutions.
The development of organic batteries with redox-organic electrode materials made from natural resources, seawater batteries with chelating agents, fiber-shaped cathodes for zinc-ion batteries, and the enhancement of power, safety, and eco-friendliness of zinc batteries are just a few examples of the progress being made.
While these technologies still face technical and economic challenges, they have the potential to play a significant role in the transition to a cleaner energy future. With continued research and innovation, the future of battery technology looks bright, and could open the way to the development of new, revolutionary technologies powered by sustainable and efficient energy storage solutions.
Interested in exploring related topics? Discover these recommended TQR articles.
- Harnessing Ocean Power: New Technologies Hold Promise for Clean and Cost-Effective Energy
- Clean Technologies and Technologies That Clean: Undoing the Climate Damage We Have Caused
- The Surprising Connection Between Human Bodies and Supernova Explosions
- A Job for the Machines: Using Artificial Intelligence to Advance Nuclear Fusion
- Chasing Nuclear Fusion
- Revolutionizing Food Production to Power a Growing World Population




This article was well organized and informative. I almost did not read it, as I was so stunned by the absurdity, in the caption to a photograph appearing at the top of the article, of the words “…it’s nearly impossible to know exactly what the technology of the future will look like.” NEARLY impossible?